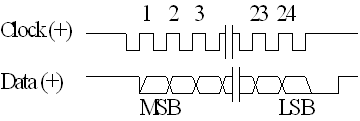
Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI) is a widely accepted controller interface. Position data from the sensor is encoded in a binary or Gray Code format and transmitted over a high-speed synchronous interface.
SSI transducers and absolute encoders offer the following advantages:
High resolution. Up to 2 µm (approx. 0.00008")
Noise immunity
Cost effective data transfer (only one 6-wire cable is needed)
Transmission rate independent of data length and resolution
Transmission over long distances
Direct connection to the RMC’s SSI interface module
Each RMC100 SSI interface module has circuitry for two SSI transducers. Each axis can be configured independently for different types of SSI transducers. To read an SSI position, the RMC sends clock pulses to the transducer, and on each rising edge of the +Clock signal, the SSI transducer places one bit of the digital position on the +Data and Data signals. The most significant bit is sent first. Below is shown a 24-bit SSI reading:
SSI Transducer
The RMC must then convert the counts returned from the transducer to an Actual Position in user-defined Position Units (usually 0.001 inch or 0.1 mm) for use in the PID control loop.
Synchronized SSI for MDTs
For motion control, MDT (Magnetostrictive Displacement Transducer) type transducers with SSI output must be of the Synchronized type. This ensures that the time between position samples matches the control loop time of the RMC controller. If the transducer is not synchronized, the sample time may not match and will adversely affect control. Make sure to specify that the transducer be of the synchronized type.
Synchronized SSI is not an issue for encoders.
See also:
Copyright (c) 1997-2015 by Delta Computer Systems, Inc.