RMC Ethernet Settings Page
To
access the Ethernet Settings Page:
In the Project pane, expand the
Modules folder, double-click the
desired CPU module and click Ethernet.
Use this page to configure the IP address
and Ethernet settings of the RMC75E, RMC150E, and RMC200. For more details
on these settings, see the Understanding
IP Addressing, RMC
Ethernet Setup and Setting
Up a Standalone TCP/IP Network topics.
IP Settings
Use this section to specify the RMC's IP Address.
The Current IP Address box will
show the RMC's current IP address settings if RMCTools is online with
the RMC.
In nearly all applications you will choose Use the following IP address option,
and enter the IP address and subnet mask.
-
Click Use the following IP address.
-
Enter an IP address and a subnet mask in dotted decimal notation (e.g. 192.168.0.5 and 255.255.255.0). To learn about IP addressing or setting up a stand-alone network, refer to Understanding IP Addressing and Setting Up a Standalone TCP/IP Network.
-
The Default Gateway is optional. If you choose not to use it, leave it blank, and the RMC will not be able to communicate with devices on networks other than its own. Otherwise, enter a value in dotted decimal notation (e.g. 192.168.0.1)
View IP Settings
for PC
If your RMC will
be running on the same network as the PC, you can click View
IP Settings for PC to view the IP settings of the network so that
you can configure the RMC's settings to be compatible.
Obtaining an IP address automatically
The RMC allows options for automatically receiving
it's IP address from a BOOTP or DHCP server. These options are not desirable
for machine control, since the server can change the RMC's IP address,
and any controlling device, such as a PLC, will not know the new address.
Or, if there is a problem with the server, the RMC will not be able to
comuunicate.
Most office networks have a DHCP server. If
you are using the RMC in an office environment for learning and setup,
you may wish to use the DHCP option to easily assign an IP address and
subnet mask.
Allow changing IP
address over Ethernet (changes over USB are always allowed)
Checking this box will allow the IP settings
to be changed through an Ethernet connection. Notice that the IP settings
can always be set via RMCTools when connected to the RMC via USB.
Notice that not allowing IP settings to be changed
via Ethernet will also prevent PLCs and HMIs from changing the IP settings
over Ethernet. As a result, the controller will no longer comply with
services in the PROFINET and EtherNet/IP protocols that change the IP
address or reset the IP settings to default values. For full PROFINET
and EtherNet/IP compliance, this box shall be checked. However, in RMC75/150
controllers prior to firmware version 3.55.0, this checkbox did not affect
PROFINET.
Not allowing the IP settings to be changed over
Ethernet prevents accidentally changing the IP settings from RMCTools
when connected over Ethernet. If they are accidentally changed, then
the connection will be broken, which can be very frustrating if programming
the RMC remotely.
Allow changing IP address from CPU display (RMC200
only)
Checking this box will allow the IP address
to be changed from the RMC200 Display Screen. If this box is unchecked,
updating the IP Address can only be viewed on the Display Screen.
Ethernet Protocol
Mode (RMC200 Only)
For EtherNet/IP I/O or PROFINET I/O communications,
the RMC200 must be set to the corresponding mode. The RMC200 requires
a mode selection in order to optimize packets for these communications.
Only one of these I/O modes may be active at any time:
-
EtherNet/IP mode
This mode is optimized for handling EtherNet/IP I/O packets. It also enables Device Level Ring (DLR) as the ring management protocol to support ring topology. PROFINET I/O connections are not supported in this mode.
-
PROFINET mode
This mode is optimized for handling PROFINET I/O packets. It also enables Media Redundancy Protocol (MRP) as the ring management protocol to support ring topology. EtherNet/IP I/O connections are not supported in this mode, but EtherNet/IP messaging is still supported.
As shown below, in each mode, all other protocols
are still fully supported, including CSP, Modbus/TCP, Mitsubishi Procedure
Exist, FINS, and DMCP.
|
Application Protocols
|
EtherNet/IP Mode
|
PROFINET Mode
|
|
EtherNet/IP Messaging
|
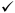
|
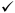
|
|
EtherNet/IP I/O
|
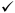
|
|
|
PROFINET I/O
|
|
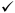
|
|
Modbus/TCP
|
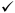
|
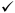
|
|
CSP (DF1 over Ethernet)
|
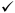
|
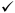
|
|
Omron FINS
|
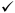
|
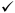
|
|
Mitsubishi Procedure Exist
|
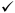
|
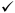
|
|
DMCP
|
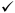
|
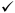
|
|
Network Management Protocols
|
EtherNet/IP Mode
|
PROFINET Mode
|
|
SNMPv1, SNMPv2c
|
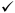
|
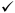
|
|
LLDP
|
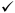
|
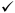
|
|
Ring Management Protocols
|
EtherNet/IP Mode
|
PROFINET Mode
|
|
DLR (Device Level Ring)
|
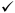
|
|
|
MRP (Media Redundancy Protocol)
|
|
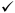
|
The current Ethernet Protocol Mode may also
be viewed from the Display Screen by browsing to Ethernet
> Protocol Mode.
Ethernet Settings
The RMC automatically detects the speed and
duplex settings of the network and uses auto-crossover (Auto-MDIX) if
necessary to match the port type (MDI/MDI-X). If you wish to manually
set these items, click Manually set speed
and duplex and choose the settings. For the RMC75/150, the manual
option will also disable auto-crossover.
The RMC200 has individual settings for each
of the two Ethernet ports, and the option to disable a port. Notice that
the RMC200 will not communicate with a 10 Mbps switch.
Additional Options
IP Address Collision Detection (ACD)
IP Address Collision Detection (ACD) is a feature
that detects duplicate IP addresses. When a device with ACD enabled is
brought online—either on power up or when the Ethernet cable is plugged
in—the device will query the network to see if its IP address is in use.
If the IP address is already in use, then the device will give up its
IP address and set its Net LED
to solid red to indicate that a duplicate IP address was detected. All
of this is done without disrupting devices already communicating on the
network.
The only downside of using ACD is that it takes
the device approximately one second longer before it is able to use its
IP address. In most applications this is an acceptable delay given the
benefits of IP ACD. However, in situations where the IP address must be
available quickly and the risk of duplicate IP addresses is deemed low,
users may elect to disable Address Collision Detection. Changes to the
IP Address Collision Detection setting requires restarting the controller
to take effect.
Delta does not recommend disabling IP Address
Collision Detection (ACD).
Allow updating firmware over Ethernet
Checking this box will allow the firmware to
be updated via Ethernet. If this box is unchecked, updating the firmware
will only be allowed via USB.
If the Allow
changing IP address over Ethernet box is not checked, then this
check box cannot be changed via Ethernet.
Communication Status
Click Open
Communication Status for a summary and statistics of the Ethernet
communications. See the Communication
Statistics topic for more details.
See Also
Ethernet
Overview
Send comments on this topic.
Copyright © 2025 Delta Computer Systems, Inc. dba Delta Motion
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()