Note: This section is intended only for new networks that will not be connected via a router to another network. If you are going to be adding an RMC to an existing network or you will be creating a new network that will be connected via a router to another network, consult your network administrator.
Note: This section assumes you have read and understood the Understanding IP Addressing topic. Please read that topic first.
Setting up a stand-alone network takes the following steps:
Wire the Network
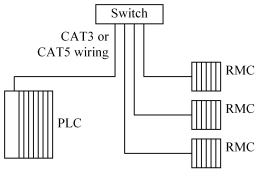
The RMC uses the IEEE 802.3 for 10BaseT hardware standard. This means it runs at 10Mbps on twisted pair wiring rated Category 3 or higher, and uses RJ45 connectors. Twisted pair networks generally use a star topology, which means that each device is wired to a single switch device:

Care should be taken to use a high-quality switch that will support your temperature, noise, vibration, and other environmental requirements. It is also important to use a switch rather than a hub to avoid collisions, which reduce the determinism of the network. Both hubs and Category 3 or 5 (commonly called CAT3 or CAT5) cabling are readily available from network supply companies.
Select a network address and subnet mask.
By convention, the network address 192.168.0 is never sent over the Internet. Therefore, it is a good choice for the network address of a stand-alone control network. Because this network address is 24 bits long, our subnet mask will be 255.255.255.0. This leaves 254 local addresses (remember that addresses 0 and 255 are reserved) for an IP address range of 192.168.0.1 to 192.168.0.254.
Assign local addresses for each device.
We now have a range of 254 IP addresses to assign. The only real requirement when assigning these addresses is to ensure that you do not assign two devices the same IP address. Therefore, it is imperative that you record your IP address assignments for use later when you need to add or replace device. By convention, local address 1 (IP address 192.168.0.1 in our new network) is used as the default gateway. We do not have a gateway/router at this time, but it is a good idea to leave that address unassigned for now.
So, assign your first device (perhaps a PLC) 192.168.0.2, assign your second device (perhaps an RMC) 192.168.0.3, etc.
Enter the network parameters into each device.
The method of assigning the network parameters varies for each type of device. Use the IP address you have assigned, a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, and leave the default gateway blank for each device. See RMC Ethernet IP Address Setup for details on editing these parameters on the RMC, and consult the manuals of the other devices on your network for details on setting up their TCP/IP parameters.
Copyright (c) 1997-2015 by Delta Computer Systems, Inc.