Note: This section assumes you have read and understood the Understanding IP Addressing topic. That topic describes the meaning of the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway parameters on this screen.
Each RMC ENET has three basic settings needed for TCP/IP communication to work: the IP address, the subnet mask, and the default gateway. The RMC ENET module allows these to be set manually or dynamically using BOOTP or DHCP. Manual configuration is recommended because the benefits of BOOTP are negligible with the RMC, and DHCP defaults to leasing an IP address. Leasing an IP address is not acceptable for industrial systems, because when the lease expires, the device will no longer be able to communicate.
There are two ways to change the TCP/IP settings in the RMC ENET module.
The first method requires an Ethernet adapter in your PC, and requires that the RMC be on the same network as your PC. Notice that the RMC ENET it not required to have valid TCP/IP settings. Therefore, you can configure and set up your RMC ENET module without ever using the serial port!
The second method requires first establishing a connection to the RMC module. Therefore, it requires either using the serial port or already having valid TCP/IP settings in the RMC ENET. It should be used when you do not have an Ethernet adapter in your PC, you are already connected to the RMC ENET module, or the RMC you want to configure is not on the same network as your PC.
To set up the RMC ENET TCP/IP settings over Ethernet:
Start RMCWin.
On the Tool menu, click Options.
Click the Communication tab.
Under Communication Drivers, click TCP/IP Direct to RMC-ENET.
Under Settings, either ensure that Autobrowse Local Network is checked or click Refresh.
You should see all RMCs on the network that your PC's Ethernet adapter is connected to. Notice that you will not see RMCs with RMC ENET firmware dated prior to 20010523, nor will you see TCP/IP-to-RS232 bridges even if they are connected to RMCs.
In the browse list, select the RMC ENET you want to configure.
If you are not sure which RMC in the list corresponds to the physical RMC you want to configure, you may have to disconnect the Ethernet cable from the RMC, wait for it to disappear from the browse list if you are using autobrowse (otherwise click Refresh), then reconnect the cable and see which device comes back onto the list.
Click Configure.
Click the option button of the desired configuration method.
If manual configuration is selected, type the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway parameters, each in dotted decimal format (e.g. 192.168.0.5). The default gateway parameter is optional.
Click OK.
RMCWin will change the TCP/IP settings in the RMC ENET module. When the update is complete, the browse list will be updated.
To set up the RMC ENET TCP/IP settings using Slot Options:
Start RMCWin.
Connect RMCWin to the RMC you want to configure. Ensure that the connection status is indicated to be "online" in the status bar. In order to connect over Ethernet, you will need valid TCP/IP settings.
On the Tools menu, click Module Configuration.
In the Slots list, click the Ethernet item.
Click Slot options.
In the Ethernet Options dialog box, click the TCP/IP tab.
Click the desired configuration method option button.
If manual configuration is selected, type the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway parameters, each in dotted decimal format (e.g. 192.168.0.5). The default gateway parameter is optional.
Click Update RMC.
The Update Module Configuration dialog box will be displayed to indicate the progress. If the module could not be reset automatically, you may be prompted to reset the module manually.
To check that the change has taken place, you can use the PING utility from any PC that has it and is on the same network.
Selecting a Configuration Method
The first decision to be made is the method you will use to configure the IP address of your device. Here are the three options selected in the TCP/IP tab of the Ethernet Options dialog box:
Manually specify an IP address
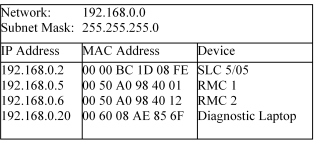
Using this method, the administrator keeps a record of all IP addresses assigned for each network, as well as the subnet mask and default gateway of the network. To use this method, click Specify an IP address, and enter each of the three parameters. If you are creating a stand-alone network, see Setting up a Stand-alone TCP/IP Control Network for suggestions on values to use, otherwise consult your network administrator. An example record for a network might look like this:

Obtain IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway from a BOOTP server.
This option causes the RMC to utilize the BOOTstrap Protocol (BOOTP) to determine its IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. When the RMC powers up, it broadcasts a request for its IP parameters. If a BOOTP server is available on the network, then the BOOTP server will look into a database of mappings from MAC addresses to IP addresses for the MAC address of the RMC that sent the request. If it finds a match, it will give the RMC an IP address, default gateway, and subnet mask. If no BOOTP server responds—either because no BOOTP server exists, or the RMC's MAC address was not found in the BOOTP server's database—the RMC's Ethernet communication channel will not be usable.
If you wish to use BOOTP, contact a network administrator for details on purchasing or obtaining a shareware BOOTP server.
Obtain IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway from a DHCP server.
This option utilizes the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to determine the IP parameters in the same way that BOOTP is used for the above option. In fact, DHCP is an extension of BOOTP and adds two features: dynamic selection of IP addresses from a pool of addresses, and lease times for addresses.
The first feature works well for many office situations because each PC can use DHCP, so there is no need for the user to enter a database of each individual IP address and MAC address. Instead, a range of IP addresses is specified, and IP addresses are assigned as they are requested. However, this does not work in industrial situations because most PLCs require that devices refer to one another by IP address. This is not possible if the IP addresses of the devices change from time to time.
The second feature is also not very usable in industrial situations. It allows each address assignment to be assigned for a limited amount of time (in hours or even days). This is intended to be used in conjunction with dynamic IP address assignment to avoid running out of addresses in the pool.
Therefore, the enhanced features of DHCP over those of BOOTP are not useful. However, DHCP still supports the one-to-one mapping of MAC addresses to IP addresses provided by BOOTP. Therefore, DHCP is offered as an alternative only to allow you to purchase either a DHCP or BOOTP server if you choose to use such a protocol.
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
These three fields are described in Understanding IP Addressing. IP Address and Subnet Mask are required parameters if you are manually configuring the RMC. Enter them in dotted decimal notation (e.g. 192.168.0.5 and 255.255.255.0). The Default Gateway parameter is optional. If you choose not to use it, leave it blank, and the RMC will not be able to communicate with devices on networks other than its own. Otherwise, enter a value in dotted decimal notation (e.g. 192.168.0.1).
LAN Settings
On the right side of the RMC TCP/IP Configuration dialog box are the TCP/IP settings for the LAN your PC's Ethernet adapter is connected to. These settings are derived from the IP address and subnet mask set up for your PC's Ethernet adapter.
If the RMC you are configuring will be running on the same network as the PC, then you should use the same subnet mask as the PC, and you should enter a TCP/IP address between the minimum and maximum addresses.
Note: The LAN Settings section is provided for convenience, but it is still necessary to take steps to ensure that the IP address you choose is unique and will remain unique. This typically involves referring to a list of IP addresses reserved on the network and recording the address that is used for the RMC on this list.
Copyright (c) 1997-2015 by Delta Computer Systems, Inc.