Default: 0
Range: 0 to 65535
The Differential Gain field is used to apply a gain based on the rate of change between the target and actual positions. There are two ways to view this.
First, this is a gain multiplied by the current rate of change in the position error. The differential drive, in millivolts is computed as follows:
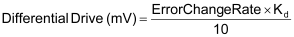

where:
|
Kd= |
Differential Gain in mV/[pos-units/ms] |
|
E0= |
position error this control loop in position units |
|
E1= |
position error last control loop in position units |
|
LoopTime = |
RMC Control Loop Time in ms (1 or 2) |
A second equivalent way of viewing this parameter is as the gain multiplied by the velocity error. When looked at from this angle, the above equations become the following:
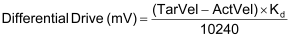
where:
|
Kd= |
Differential Gain in mV/[pos-units/s] |
|
TarVel = |
target velocity in pos-units/s |
|
ActVel = |
actual velocity in pos-units/s |
Note: The actual drive output may be reduced based on the values of the Extend Feed Forward and Retract Feed Forward.
CAUTION: To avoid oscillation during initial tuning start with values below 10.
Why Bother?
The Differential Gain field will usually be set to zero. Noisy or low-resolution feedback will limit the amount the Differential Gain can be increased.
Copyright (c) 1997-2015 by Delta Computer Systems, Inc.